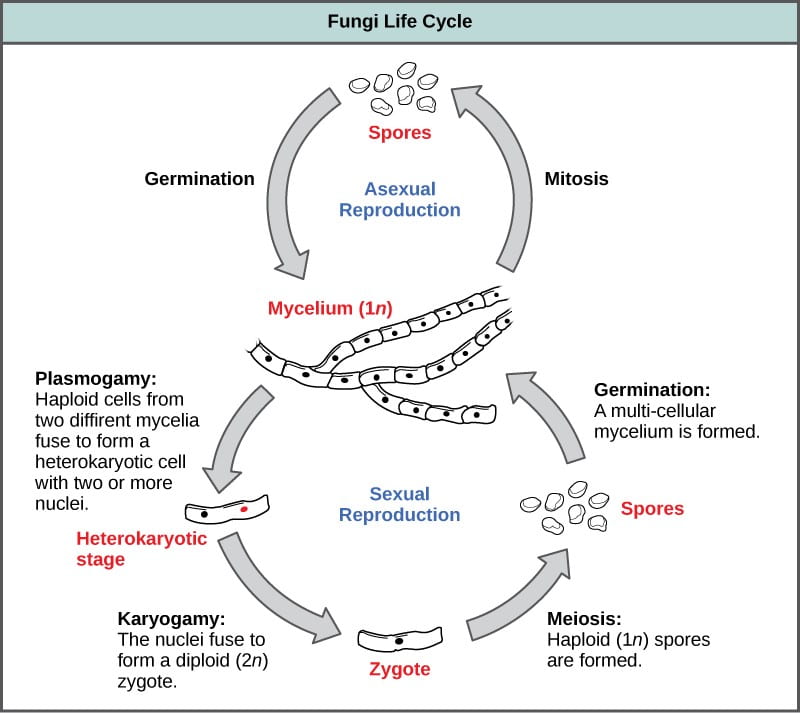
fungi life cycle explained
For most of the molds indoors fungi are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle. The haploid phase is the predominant phase of the life cycle.

Characteristics Of Fungi Openstax Biology 2e
Despite their diversity in many features the Ascomycetes possess certain common unifying characteristics namely the somatic body composed of a loose indefinite mass of septate mycelium.

. Fungi need to produce so many spores because most spores simply die where they land lacking water and food. Fungi are eukaryotic organisms and include yeasts moulds and mushrooms. Life Cycle of Fungi.
Fungi replicate sexually andor asexually. The organism is haploid and has no diploid phase except for the sexual sporangium. While some fungi reproduce sexually others reproduce asexually.
Spores produced both. Brundrett 1990 showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative diagram of the developmental stages of a mould. Here the haploid spores produced from zygote germinate to produce haploid mycelia.
Therefore dimorphic fungi possess two kinds of. A number of fungi have lost the capacity for sexual reproduction and reproduce by asexual spores or by vegetative growth only. One of these migrates into the germ tube.
The elementary flow of biogenic CO 2 absorption by water reeds is of particular significance for our discussion. The Basidiomycota basidiomycetes are fungi that have basidia club-shaped structures that produce basidiospores spores produced through budding within fruiting bodies called. The single nucleus of the resting spore divides early in germination.
These are called sporangiophores. Fungi lack chlorophyll and hence cannot perform photosynthesis. Some fungal colonies can grow for a very long time and over a very large area.
But this model provides a good overview in terms of how fungi grows from birth to death. Most of the molds indoors are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle. The life cycle of an ascomycete is characterized by the production of asci during the sexual phase.
The fungi which reproduce sexually have alternating haploid and diploid phases. This is where spores come in which are dispersed by wind and can produce a new mycelium. In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of ascomycetes explained with the help of a suitable diagram.
The life cycle of fungi has many different patterns based on the species of the fungi. To form n gametes n. With the elongation of the germ tube most of the mitochondria migrate into it and become concentrated near the tip.
Spore germ hypha mature mycelium. The mode of asexrual reproduction. It involves the fusion of the hyphae of two different individuals into a mycelium.
There are four basic steps in the life cycle of a fungi. In reality there are many sub-steps of the process. We present details of this process here.
The life cycle inventory phase involves the compilation of elementary flow data ie flows that pass between the system boundary and the natural environment. Perfect fungi are sexually and asexually replicated whereas imperfect fungi are only asexually reproduced by mitosis. In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase.
Terms in this set 21 Fungi unique for. Fungus Life Cycle. Many fungi need two of these colonies to grow next to each other and to mate before that fungus is able to form any new spores and so spread further.
The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion and the diploid phase begins with the formation of the zygote the diploid cell resulting from fusion of two haploid sex cells. Spore germ hypha mature mycelium. In both sexual and asexual reproduction fungi develop spores that either fly on the wind or take a ride on an animal dispersing from the parent organism.
Some fungi especially the chytrids and zygomycetes have a life cycle more like that found in many protists. This is the first stage in the life cycle of a fungus. The Life Cycle of Fungi.
The mycelium contains haploid nuclei from both specimens. Fungus reproduction is not very romantic. The resulting cells may sometimes stick together as a short chain or pseudohypha Figure 525.
By producing vast numbers of spores both sexually and asexually so in TWO parts of life cycle Major difference from plants. The majority of mold fungi do not have sexual stages and following this simple life cycle pattern. All fungi begin their life cycle in this stage.
The generalized life cycle of fungi. Not all fungi reproduce in the same way. Meiosis reduction division restores the haploid number of chromosomes and initiates the.
The electron-dense wall layer W 2 remains at the base of the germ tube and around the spore. Haploid hyphae produce gametes which fuse by plasmogamy and karyogamy to produce diploid zygote. Life cycle of fungi.

Life Cycle Of An Am Fungus And The Different Steps During Am Development Download Scientific Diagram
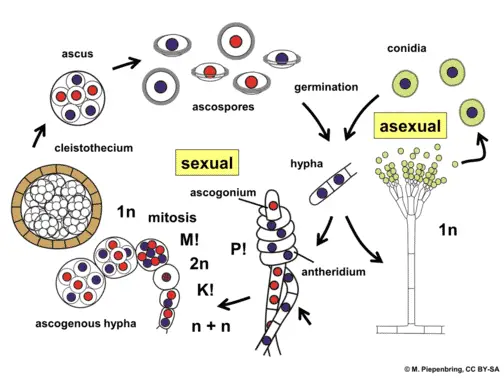
Fungi Explained Here Is What You Need To Know Microscope Clarity

Life Cycle Of Saprolegnia With Diagram Oomycetes

Zygomycota The Conjugated Fungi Biology For Majors Ii

Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Worldkids
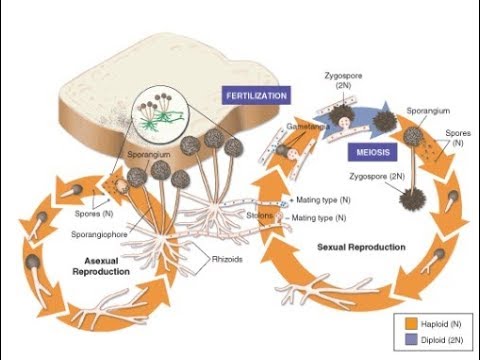
Life Cycle Of Fungus Black Bread Mold Rhizopus Stolonifer Youtube

Reproduction In Fungi Life Cycle Of Fungi Youtube

The Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Teelixir

24 1c Fungi Reproduction Biology Libretexts

Ascomycota The Sac Fungi Biology For Majors Ii

A Detailed Explanation Of The Mushroom Life Cycle Grocycle

Fungi Reproductive Cycle Diagram Quizlet
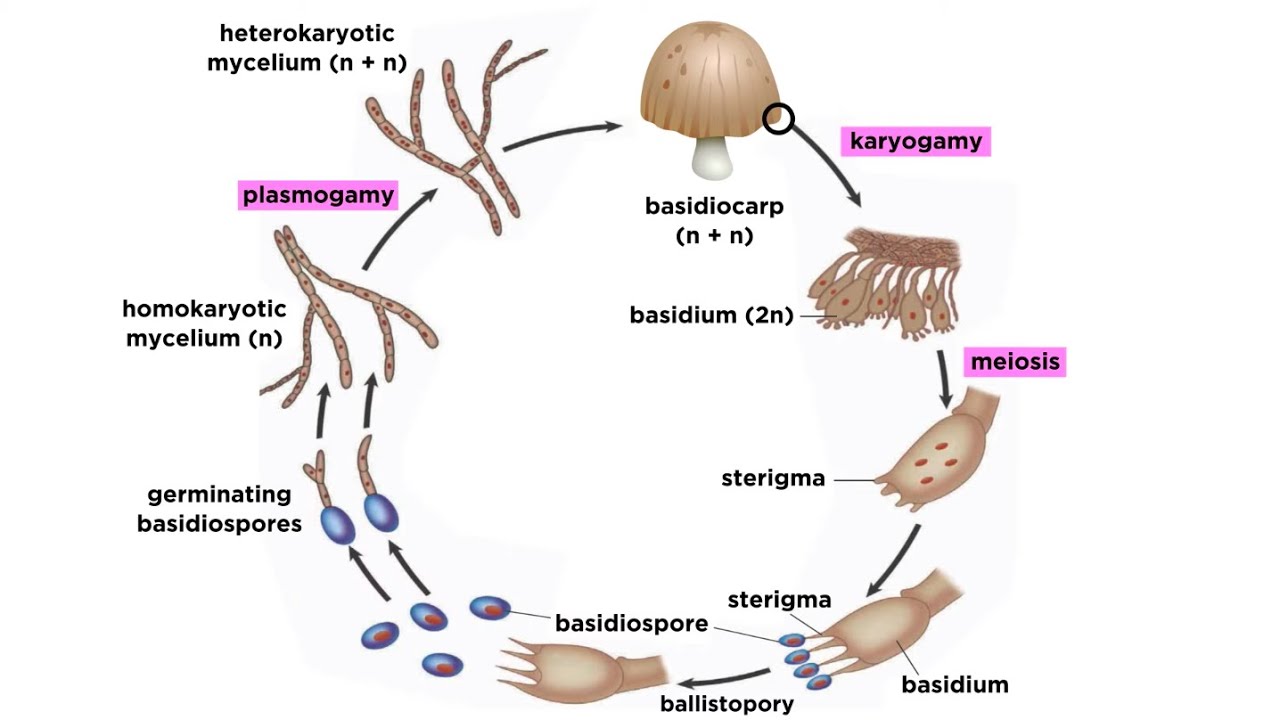
Basidiomycota Part 2 The Mushroom Life Cycle Youtube

11 6 Sexual Reproduction Life Cycles Of Sexually Reproducing Organisms Biology Libretexts